REDUCED NETWORK TRAFFIC
One network will not access the data of other network without the use of router. Thus we can reduce the amount of data remain in one network. Less data less overhead, collision, or broadcast storm.
OPTIMIZED NETWORK PERFORMANCE
This is a result of reduced network traffic.
SIMPLIFIED MANAGEMENT
It's easier to identify and isolate network problems in a group of Smaller connected networks than within one gigantic network. Facilitated spanning of large geographical distances Because WAN links are significantly slower and more expensive than LAN links, a single large network that spans long distances can create problems in every area earlier listed. Connecting multiple smaller networks makes the system more efficient.
Powers of 2
Powers of 2 are important to understand and memorize for use with IP subnetting.
Subnet mask
A subnet mask is a 32-bit value that allows the receiver of IP packets to distinguish the network ID portion of the IP address from the host ID portion of the IP address. Every IP address is composed of a network component and a host component. The subnet mask has a single purpose: to identify which part of an IP address is the network component and which part is the host component. Subnet mask value 0 represent host ID while subnet mask value 1 to 255 represents Network ID in ip address
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR)
This slash notation is sometimes called CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) notation. It's basically the method that ISPs (Internet service providers) use to allocate a number of Addresses to a company, a home—a customer. The slash notation is simply the number of 1s in a row in the subnet mask. The real reason to use CIDR notation is simply that it is easier to say and especially to type.
Address Class and Default Mask
Subnetting happens when we extend the subnet mask past the default boundary for the address we are working with. So it's obvious that we first need to be sure of what the default mask is supposed to be for any given address. When faced with a subnetting question, the first thing to do is decide what class the address belongs to. And later decide what the default subnet mask is. One of the rules that Cisco devices follow is that a subnet mask must be a contiguous string of 1s followed by a contiguous string of 0s. There are no exceptions to this rule: A valid mask is always a string of 1s, followed by 0s to fill up the rest of the 32 bits. (There is no such rule in the real world, but we will stick to the Cisco rules here—it's a Cisco exam, after all.) Therefore, the only possible valid values in any given octet of a subnet mask are 0, 128, 192, 224, 240, 248, 252, 254, and 255. Any other value is invalid.
Network ID and Broadcast ID
The first address in a network number is called the network address, or wire number. This address is used to uniquely identify one segment or broadcast domain from all the other segments in the network.
The Broadcast ID
The last address in the network number is called the directed broadcast address and is used to represent all hosts on this network segment. it is the common address of all hosts on that Network ID. This should not be confused with a full IP broadcast to the address of 255.255.255.255, which hits every IP host that can hear it; the Broadcast ID hits only hosts on a common subnet. A directed broadcast is similar to a local broadcast.
The main difference is that routers will not propagate local broadcasts between segments, but they will, by default, propagate directed broadcasts.
The last address in the network number is called the directed broadcast address and is used to represent all hosts on this network segment. it is the common address of all hosts on that Network ID. This should not be confused with a full IP broadcast to the address of 255.255.255.255, which hits every IP host that can hear it; the Broadcast ID hits only hosts on a common subnet. A directed broadcast is similar to a local broadcast.
The main difference is that routers will not propagate local broadcasts between segments, but they will, by default, propagate directed broadcasts.
Host Addresses
Any address between the network address and the directed broadcast address is called a host address for the segment. You assign these middle addresses to host devices on the segment, such as PCs, servers, routers, and switches.
IP ROUTING
ROUTING
Routers use a routing table to accomplish the task of forwarding the packets properly throughout an internetwork.
There are three different ways a routing table is built:
- Statically
- Default
- Dynamically
A. Statically or Static Routing:
Static routing is not really a routing protocol. Static routing is simply the process of manually entering routes into a device’s routing table via a configuration file that is loaded when the routing device starts up. Static routing is the simplest form of routing, but it is a manual process.
B. Default:
A default route, also known as the gateway of last resort, is the network route used by a router when no other known route exists for a given IP packet’s destination address.
C. Dynamically or Dynamic Routing:
Routing that adjusts automatically to network topology or traffic change also called as adaptive routing. Dynamic routing protocols will then distribute this ‘best route’ information to other routers running the same routing protocol, thereby extending the information on what networks exist and can be reached. This gives dynamic routing protocols the ability to adapt to logical network topology changes.
640-802 CCNA® Exam Topics (Blueprint)
640-802 CCNA® Exam Topics
Exam Description
The 640-802 CCNA is the composite exam associated with the Cisco Certified Network Associate certification. Candidates can prepare for this exam by taking the Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1) v1.0 and the Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2) v1.0 courses. This exam tests a candidate's knowledge and skills required to install, operate, and troubleshoot a small to medium size enterprise branch network. The topics include connecting to a WAN; implementing network security; network types; network media; routing and switching fundamentals; the TCP/IP and OSI models; IP addressing; WAN technologies; operating and configuring IOS devices; extending switched networks with VLANs; determining IP routes; managing IP traffic with access lists; establishing point-to-point connections; and establishing Frame Relay connections.
Exam Topics
The following topics are general guidelines for the content likely to be included on the Cisco Certified Network Associate exam. However, other related topics may also appear on any specific delivery of the exam. In order to better reflect the contents of the exam and for clarity purposes, the guidelines below may change at any time without notice.
Describe how a network works
- Describe the purpose and functions of various network devices
- Select the components required to meet a network specification
- Use the OSI and TCP/IP models and their associated protocols to explain how data flows in a network
- Describe common networked applications including web applications
- Describe the purpose and basic operation of the protocols in the OSI and TCP models
- Describe the impact of applications such as Voice Over IP on a network
- Interpret network diagrams
- Determine the path between two hosts across a network
- Describe the components required for network and Internet communications
- Identify and correct common network problems at layers 1, 2, 3 and 7 using a layered model approach
- Differentiate between LAN/WAN operation and features
Configure, verify and troubleshoot a switch with VLANs and interswitch communications
- Select the appropriate media, cables, ports, and connectors to connect switches to other network devices and hosts
- Explain the technology and media access control method for Ethernet networks
- Explain network segmentation and basic traffic management concepts
- Explain basic switching concepts and the operation of Cisco switches
- Perform and verify initial switch configuration tasks including remote access management
- Verify network status and switch operation using basic utilities (including: ping, traceroute, telnet, SSH, arp, ipconfig), and SHOW & DEBUG commands
- Identify, prescribe, and resolve common switched network media issues, configuration issues, auto negotiation, and switch hardware failures
- Describe enhanced switching technologies (including: VTP, RSTP, VLAN, PVSTP, 802.1q)
- Describe how VLANs create logically separate networks and the need for routing between them
- Configure, verify, and troubleshoot VLANs
- Configure, verify, and troubleshoot trunking on Cisco switches
- Configure, verify, and troubleshoot interVLAN routing
- Configure, verify, and troubleshoot VTP
- Configure, verify, and troubleshoot RSTP operation
- Interpret the output of various show and debug commands to verify the operational status of a Cisco switched network.
- Implement basic switch security (including: port security, trunk access, management vlan other than vlan1, etc.)
Implement an IP addressing scheme and IP Services to meet network requirements in a medium-size Enterprise branch office network
- Describe the operation and benefits of using private and public IP addressing
- Explain the operation and benefits of using DHCP and DNS
- Configure, verify and troubleshoot DHCP and DNS operation on a router (using both the CLI and SDM)
- Implement static and dynamic addressing services for hosts in a LAN environment
- Calculate and apply an addressing scheme including VLSM IP addressing to a network
- Determine the appropriate classless addressing scheme using VLSM and summarization to satisfy addressing requirements in a LAN/WAN environment
- Describe the technological requirements for running IPv6 in conjunction with IPv4 (including: protocols, dual stack, tunneling, etc).
- Describe IPv6 addresses
- Identify and correct common problems associated with IP addressing and host configurations
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot basic router operation and routing on Cisco devices
- Describe basic routing concepts (including: packet forwarding, router lookup process)
- Describe the operation of Cisco routers (including: router bootup process, POST, router components)
- Select the appropriate media, cables, ports, and connectors to connect routers to other network devices and hosts
- Configure, verify, and troubleshoot RIPv2
- Access and utilize the router to set basic parameters.(including: CLI/SDM)
- Connect, configure, and verify operation status of a device interface
- Verify device configuration and network connectivity using ping, traceroute, telnet, SSH or other utilities
- Perform and verify routing configuration tasks for a static or default route given specific routing requirements
- Manage IOS configuration files. (including: save, edit, upgrade, restore)
- Manage Cisco IOS
- Compare and contrast methods of routing and routing protocols
- Configure, verify, and troubleshoot OSPF
- Configure, verify, and troubleshoot EIGRP
- Verify network connectivity (including: using ping, traceroute, and telnet or SSH)
- Troubleshoot routing issues
- Verify router hardware and software operation using SHOW & DEBUG commands.
- Implement basic router security
Explain and select the appropriate administrative tasks required for a WLAN
- Describe standards associated with wireless media (including: IEEE, WI-FI Alliance, ITU/FCC)
- Identify and describe the purpose of the components in a small wireless network. (Including: SSID, BSS, ESS)
- Identify the basic parameters to configure on a wireless network to ensure that devices connect to the correct access point
- Compare and contrast wireless security features and capabilities of WPA security (including: open, WEP, WPA-1/2)
- Identify common issues with implementing wireless networks. (Including: Interface, misconfiguration)
Identify security threats to a network and describe general methods to mitigate those threats
- Describe today's increasing network security threats and explain the need to implement a comprehensive security policy to mitigate the threats
- Explain general methods to mitigate common security threats to network devices, hosts, and applications
- Describe the functions of common security appliances and applications
- Describe security recommended practices including initial steps to secure network devices
Implement, verify, and troubleshoot NAT and ACLs in a medium-size Enterprise branch office network
- Describe the purpose and types of ACLs
- Configure and apply ACLs based on network filtering requirements using SDM and CLI
- Configure and apply an ACL to limit telnet and SSH access to the router using SDM and CLI
- Verify and monitor ACLs in a network environment
- Troubleshoot ACL issues
- Explain the basic operation of NAT
- Configure NAT for given network requirements using SDM and CLI
- Troubleshoot NAT issues
Implement and verify WAN links
- Describe different methods for connecting to a WAN
- Configure and verify a basic WAN serial connection
- Configure and verify Frame Relay on Cisco routers
- Troubleshoot WAN implementation issues
- Describe VPN technology (including: importance, benefits, role, impact, components)
- Configure and verify a PPP connection between Cisco routers
CCNA – Basic Questions 2
Question 1

Here you will find answers to Basic Questions – Part 2
Question 1What are some of the advantages of using a router to segment the network? (Choose two)
A. Filtering can occur based on Layer 3 information.
B. Broadcasts are eliminated.
C. Routers generally cost less than switches.
D. Broadcasts are not forwarded across the router.
E. Adding a router to the network decreases latency.
B. Broadcasts are eliminated.
C. Routers generally cost less than switches.
D. Broadcasts are not forwarded across the router.
E. Adding a router to the network decreases latency.
Answer: A D
Question 2
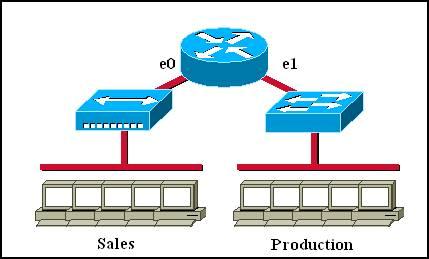
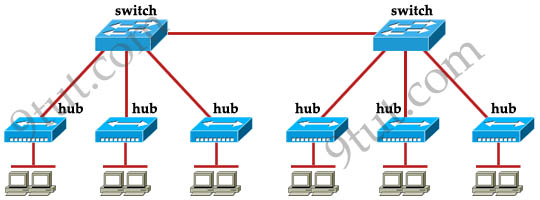
Which of the following statements describe the network shown in the graphic? (Choose two)

A. There are two broadcast domains in the network.
B. There are four broadcast domains in the network.
C. There are six broadcast domains in the network.
D. There are four collision domains in the network.
E. There are five collision domains in the network.
F. There are seven collision domains in the network.
B. There are four broadcast domains in the network.
C. There are six broadcast domains in the network.
D. There are four collision domains in the network.
E. There are five collision domains in the network.
F. There are seven collision domains in the network.
Answer: A F
Explanation
Only router can break up broadcast domains so in the exhibit there are 2 broadcast domains: from e0 interface to the left is a broadcast domain and from e1 interface to the right is another broadcast domain -> A is correct.
Both router and switch can break up collision domains so there is only 1 collision domain on the left of the router (because hub doesn’t break up collision domain) and there are 6 collision domains on the right of the router (1 collision domain from e1 interface to the switch + 5 collision domains for 5 PCs in Production) -> F is correct.
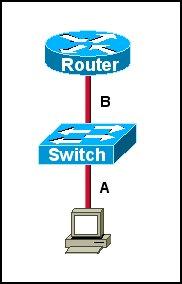
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. The two connected ports on the switch are not turning orange or green. What would be the most effective steps to troubleshoot this physical layer problem? (Choose three)

A. Ensure that the Ethernet encapsulations match on the interconnected router and switch ports.
B. Ensure that cables A and B are straight-through cables.
C. Ensure cable A is plugged into a trunk port.
D. Ensure the switch has power.
E. Reboot all of the devices.
F. Reseat all cables.
B. Ensure that cables A and B are straight-through cables.
C. Ensure cable A is plugged into a trunk port.
D. Ensure the switch has power.
E. Reboot all of the devices.
F. Reseat all cables.
Answer: B D F
Explanation
The ports on the switch are not up indicating it is a layer 1 (physical) problem so we should check cable type, power and how they are plugged in.
Question 4
For what two purposes does the Ethernet protocol use physical addresses? (Choose two)
A. to uniquely identify devices at Layer 2
B. to allow communication with devices on a different network
C. to differentiate a Layer 2 frame from a Layer 3 packet
D. to establish a priority system to determine which device gets to transmit first
E. to allow communication between different devices on the same network
F. to allow detection of a remote device when its physical address is unknown
B. to allow communication with devices on a different network
C. to differentiate a Layer 2 frame from a Layer 3 packet
D. to establish a priority system to determine which device gets to transmit first
E. to allow communication between different devices on the same network
F. to allow detection of a remote device when its physical address is unknown
Answer: A E
Explanation
Physical addresses or MAC addresses are used to identify devices at layer 2 -> A is correct.
MAC addresses are only used to communicate on the same network. To communicate on different network we have to use Layer 3 addresses (IP addresses) -> B is not correct; E is correct.
Layer 2 frame and Layer 3 packet can be recognized via headers. Layer 3 packet also contains physical address -> C is not correct.
On Ethernet, each frame has the same priority to transmit by default -> D is not correct.
All devices need a physical address to identify itself. If not, they can not communicate -> F is not correct.
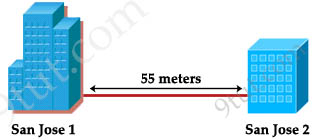
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. Two buildings on the San Jose campus of a small company must be connected to use Ethernet with a bandwidth of at least 100 Mbps. The company is concerned about possible problems from voltage potential difference between the two buildings. Which media type should be used for the connection?

A. UTP cable
B. STP cable
C. Coaxial cable
D. Fiber optic cable
B. STP cable
C. Coaxial cable
D. Fiber optic cable
Answer: D
Explanation
Because the company has problem about voltage potential difference between the two buildings so they should connect via fiber optic cable which uses light pulses to transmit information instead of using electronic pulses.
Question 6
Which command can be used from a PC to verify the connectivity between host that connect through path?
A. tracert address
B. ping address
C. arp address
D. traceroute address
B. ping address
C. arp address
D. traceroute address
Answer: A
Explanation
To check the connectivity between a host and a destination (through some networks) we can use both “tracert” and “ping” commands. But the difference between these 2 commands is the “tracert” command can display a list of near-side router interfaces in the path between the source and the destination. Therefore the best answer in this case is A – tracert address.
Note: “traceroute” command has the same function of the “tracert” command but it is used on Cisco routers only, not on a PC.
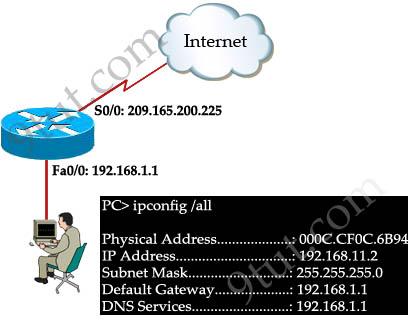
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer is troubleshooting an internet connectivity problem on the computer. What causing the problem?

A. wrong DNS server
B. wrong default gateway
C. incorrect IP address
D. incorrect subnet mask
B. wrong default gateway
C. incorrect IP address
D. incorrect subnet mask
Answer: C
Explanation
The IP address of the PC (192.168.11.2/24) is not on the same network with its gateway 192.168.1.1 -> C is correct.
Question 8
How many broadcast domains are shown in the graphic assuming only the default vlan is configured on the switches?

A. one
B. six
C. twelve
D. two
B. six
C. twelve
D. two
Answer: A
Explanation
Only router can break up broadcast domains but in this exhibit no router is used so there is only 1 broadcast domain.
For your information, there are 7 collision domains in this exhibit (6 collision domains between hubs & switches + 1 collision between the two switches).
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit.
PC> tracert 10.16.176.23
Tracing route to 10.16.176.23 over a maximum of 30 hops
1 31 ms 31 ms 32ms 172.16.182.1
2 62 ms 62 ms 62 ms 192.1681.6 3 93 ms 92 ms 34 ms 192.168.1.10 4 125 ms 110ms 125ms 10.16.176.23
Trace complete.
|
Host A has tested connectivity to a remote network. What is the default gateway for host A?
A. 172.16.182.1
B. 192.168.1.1
C. 10.16.176.1
D. 192.168.1.6
B. 192.168.1.1
C. 10.16.176.1
D. 192.168.1.6
Answer: A
Explanation
It will list all the routers (from nearest to farthest) it passes through until it reaches its destination so the first hop is its nearest IP. If we ping from a PC, it is also the default gateway for that PC -> A is correct.
Question 10
What functions do routers perform in a network? (Choose two)
A. packet switching
B. access layer security
C. path selection
D. VLAN membership assignment
E. bridging between LAN segments
F. microsegmentation of broadcast domains
B. access layer security
C. path selection
D. VLAN membership assignment
E. bridging between LAN segments
F. microsegmentation of broadcast domains
CCNA – Basic Questions
Question 1
For which type of connection should a straight-through cable be used?
A. switch to switch
B. switch to hub
C. switch to router
D. hub to hub
E. router to PC
B. switch to hub
C. switch to router
D. hub to hub
E. router to PC
Answer: C
Explanation
To specify when we use crossover cable or straight-through cable, we should remember:
Group 1: Router, Host, Server
Group 2: Hub, Switch
One device in group 1 + One device in group 2: use straight-through cable
Two devices in the same group: use crossover cable
Group 2: Hub, Switch
One device in group 1 + One device in group 2: use straight-through cable
Two devices in the same group: use crossover cable
In this case we can use straight-through cable to connect a switch to a router -> C is correct.
Question 2
Which type of cable is used to connect the COM port of a host to the COM port of a router or switch?
A. crossover
B. straight-through
C. rolled
D. shielded twisted-pair
B. straight-through
C. rolled
D. shielded twisted-pair
Answer: C
Explanation
The correct question should be “Which type of cable is used to connect the COM port of a host to the CONSOLE port of a router or switch?” and the correct answer is rollover cable. But we can’t plug this rollover cable directly into our host because it will not work. We often use a RJ45 to DB9 Female cable converter as shown below:

Question 3
What is the first 24 bits in a MAC address called?
A. NIC
B. BIA
C. OUI
D. VAI
B. BIA
C. OUI
D. VAI
Answer: C
Explanation
Organizational Unique Identifier (OUI) is the first 24 bits of a MAC address for a network device, which indicates the specific vendor for that device as assigned by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Incorporated (IEEE). This identifier uniquely identifies a vendor, manufacturer, or an organization.
Question 4
In an Ethernet network, under what two scenarios can devices transmit? (Choose two)
A. when they receive a special token
B. when there is a carrier
C. when they detect no other devices are sending
D. when the medium is idle
E. when the server grants access
B. when there is a carrier
C. when they detect no other devices are sending
D. when the medium is idle
E. when the server grants access
Answer: C D
Explanation
Ethernet network is a shared environment so all devices have the right to access to the medium. If more than one device transmits simultaneously, the signals collide and can not reach the destination.
If a device detects another device is sending, it will wait for a specified amount of time before attempting to transmit.
When there is no traffic detected, a device will transmit its message. While this transmission is occurring, the device continues to listen for traffic or collisions on the LAN. After the message is sent, the device returns to its default listening mode.
So we can see C and D are the correct answers. But in fact “answer C – when they detect no other devices are sending” and “when the medium is idle” are nearly the same.
Question 5
Which two benefits are provided by using a hierarchical addressing network addressing scheme? (Choose two)
A. reduces routing table entries
B. auto-negotiation of media rates
C. efficient utilization of MAC addresses
D. dedicated communications between devices
E. ease of management and troubleshooting
B. auto-negotiation of media rates
C. efficient utilization of MAC addresses
D. dedicated communications between devices
E. ease of management and troubleshooting
Answer: A E
Question 6
When a host transmits data across a network to another host, which process does the data go through?
A. standardization
B. conversion
C. encapsulation
D. synchronization
B. conversion
C. encapsulation
D. synchronization
Answer: C
Explanation
To transmit to another host, a host must go through the TCP/IP model (very similar to the OSI model). At each layer, the message is encapsulated with that layer’s header (and trailer if it has). This process is called encapsulation.
Question 7
Which two Ethernet fiber-optic modes support distances of greater than 550 meters?
A. 1000BASE-CX
B. 100BASE-FX
C. 1000BASE-LX
D. 1000BASE-SX
E. 1000BASE-ZX
B. 100BASE-FX
C. 1000BASE-LX
D. 1000BASE-SX
E. 1000BASE-ZX
Answer: C E
Explanation
Below lists the cabling standards mentioned above
| Standard | Cabling | Maximum length |
| 1000BASE-CX | Twinaxial cabling | 25 meters |
| 100BASE-FX | Two strands, multimode | 400 m |
| 1000BASE-LX | Long-wavelength laser, MM or SM fiber | 10 km (SM) 3 km (MM) |
| 1000BASE-SX | Short-wavelength laser, MM fiber | 220 m with 62.5-micron fiber; 550 m with 50-micron fiber |
| 1000BASE-ZX | Extended wavelength, SM fiber | 100 km |
Note:
+ MM: Multimode
+ SM: Single-mode
+ SM: Single-mode
(Reference: The official self-study test preparation guide to the Cisco CCNA INTRO exam 640-821)
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. What type of connection would be supported by the cable diagram shown?
| Pin | Color | Function | Pin | Color | Function |
| 1 | White/Green | TX+ | 1 | White/Green | TX+ |
| 2 | Green | TX- | 2 | Green | TX- |
| 3 | White/Orange | RX+ | 3 | White/Orange | RX+ |
| 6 | Orange | RX- | 6 | Orange | RX- |
A. PC to router
B. PC to switch
C. server to router
D. router to router
B. PC to switch
C. server to router
D. router to router
Answer: B
Explanation
From the “Pin” and “Color” in the exhibit we know that this is a straight-through cable so it can be used to connect PC to switch.
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. What type of connection would be supported by the cable diagram shown?
| Pin | Color | Function | Pin | Color | Function |
| 1 | White/Green | TX+ | 3 | White/Green | RX+ |
| 2 | Green | TX- | 6 | Green | RX- |
| 3 | White/Orange | RX+ | 1 | White/Orange | TX+ |
| 6 | Orange | RX- | 2 | Orange | TX- |
A. PC to router
B. PC to switch
C. server to switch
D. switch to router
B. PC to switch
C. server to switch
D. switch to router
Answer: A
Explanation
This is a crossover cable so it can be used to connect PC and router.

Question 10
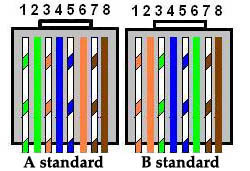
Which two topologies are using the correct type of twisted-pair cables? (Choose two)
A. 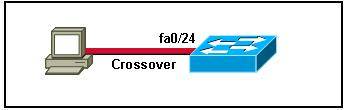

B. 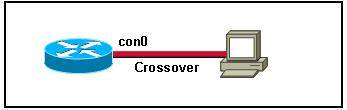

C. 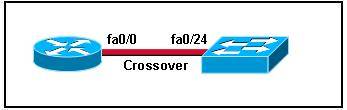

D. 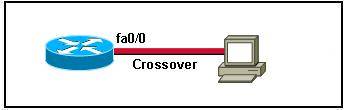

E. 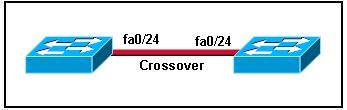

Answer: D E
KEEP SHARING AND VISITING :) :)















